How To Run Windows 8 Faster
How to boost Windows 8 performance
Get to know Windows 8's built-in tools for troubleshooting and speeding upwards your PC
At that place'southward an unassailable dominion of computing: No matter how fast your figurer is, and no matter how well it runs, y'all desire it to run better.
If yous're looking to improve Windows 8, assist is on the mode. I've rounded upwardly my favorite tips for doing arrangement analysis, troubleshooting and fixing whatsoever bug you find, and in general speeding things upwardly. No extra software is required; everything y'all need is built right into Windows 8.
If y'all've been effectually the Windows block a few times, you probably call up having to manually crank through an assortment of functioning-oriented tasks: mucking effectually with page files, editing the Registry or using third-party tools such as disk cleaners. But over the years Windows has gotten much better at automating many of those tasks. In Windows 8, generally the best way to improve functioning and know what's going on in your system is to utilize Windows' born tools, including the Resource Monitor, the Task Manager and the Reliability Monitor.
For some reason, however, several of the most useful administrative tools are subconscious past default, then the offset thing to do is unhide them: Press the Windows key + I to open the Settings charm, click the word Tiles, and then change the "Show administrative tools" slider to Yes.
With these subconscious gems revealed, we can go started.
For more useful tips, see 10 Windows 8 tips, tricks and hacks. If you demand assist getting upwardly to speed with Windows 8, encounter Windows viii cheat sail.
Troubleshoot lethargy with the Resource Monitor
A little-known tool called the Resource Monitor does a very good job of tracking down operation issues and fixing them. Although it's not new -- it's been included in Windows since Vista -- it's still a great way to observe out nearly the resources your system uses and to see what applications and services are making the most use of your arrangement. Based on that, you can decide which apps and services to shut down and which to continue running.
To run information technology, blazon resmon at the Start screen so click the resmon.exe icon that appears on the left side of the screen under Apps.
Note: If y'all're using a visitor-owned PC and don't take Administrator privileges, you lot may not be able to run the Resource Monitor. But never fright: Y'all tin can still use the Task Director and about other tools covered in this story to troubleshoot performance bug.
If you are able to get into the Resource Monitor, outset on the Overview tab. It offers a snapshot of your organization'south resource usage, including CPU use, disk use, network utilise and retention utilise.
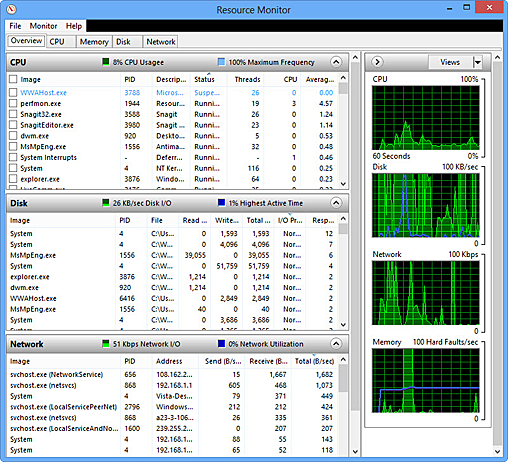
The screen is divided into two. On the left-mitt side you'll see every process running on your organisation, by resource category (CPU, Disk, Network, and Memory), along with details most the usage of each procedure. (A procedure is any programme that runs in Windows, from a tiny background task to a complex awarding such every bit a Web browser.)
On the right-manus side you'll see moving graphs of their cumulative utilise over time. Y'all tin can see at a glance whether your CPU, deejay, network or retentivity utilise is maxing out. If any are, you know you've got a trouble, and you know the full general category of problem.
For more details about any of those categories, click the appropriate tab beyond the top of the Resources Monitor. Each tab shows you what applications or services are making use of that particular resource, forth with other useful information. For example, the CPU tab shows all the apps and services using the CPU, with a running average of CPU employ for each app and service. Those that employ the CPU the most are listed at the pinnacle; those that use it the least are listed at the bottom.
The brandish in each tab varies co-ordinate to what'southward most useful. For instance, the Retentivity tab shows, in add-on to what programs and services are using retention, how much memory is currently used, cached, reserved for hardware and so on.
Once you've zeroed in on the problem, yous tin do something about it. If you've got apps and services overtaxing your CPU, for instance, you can close any of them by correct-clicking it and selecting End Procedure from the drop-down menu. You might also consider looking for alternatives to those apps and services, and then using Resources Monitor subsequently on to encounter whether those alternatives have lower resource usage.
Note that most of the data that the Resources Monitor displays is also shown in the Chore Manager, another built-in functioning tool we'll cover afterwards in this article. Redone for Windows 8, the Chore Manager has a more comprehensive set of tools and information than the Resource Monitor. That said, the Resource Monitor is yet a useful tool for troubleshooting operation problems considering it offers a quick at-a-glance expect at your system, with in-depth data on each of its tabs.
Track stability and troubleshoot crashes with the Reliability Monitor
Another useful Windows tool is the Reliability Monitor, beginning introduced in Windows Vista. It offers a historical view of overall arrangement stability and even includes detailed data nigh system crashes. Armed with this information, you lot can pinpoint the sources of bug and accept steps to eliminate them.
To launch the Reliability Monitor, type reliability at the Start screen, click Settings, and click the "View reliability history" icon that appears on the left nether Settings. The blue line running across the graph shows your system's stability over fourth dimension. It's based on a number that Windows calculates to guess your system's overall reliability. The maximum is 10 and the minimum is one.
Every time in that location's a system failure, application failure or similar result, the index drops, sometimes sharply -- particularly if there'due south been more than than one failure in a mean solar day. Each day your system doesn't have a failure, the index rises a picayune bit.
On days at that place are failures, yous'll come across red icons, divided into rows by blazon of failure -- application, Windows or miscellaneous (hardware, drivers, etc.). The chart as well has icons for warnings nearly unsuccessful updates and for data nigh successful updates and installations.

Select any day with a failure or other event, and at the bottom of the screen you'll see details nigh those events, divided into categories. Pay attending to the details of each crash and failure. Look for patterns, such as if the same awarding ofttimes crashes. If so, uninstall it, or look for an update that fixes the trouble.
Finally, downwardly at the very lesser of the screen click "View all trouble reports." Rather than seeing a chart over fourth dimension, yous'll instead see a list of all of your bug, including summaries. It lets you scroll through your bug more quickly than in the normal view, because they're in a long, vertical list.
Generate a detailed Performance Monitor report
Windows 8 includes a Performance Monitor tool that shows an immense amount of item about a organisation'due south hardware and software. Unfortunately, its main interface is almost incommunicable to decipher. There is, however, ane way to become some very useful information out of the Performance Monitor -- tell it to generate a detailed report for you that pinpoints arrangement issues and suggests fixes.
Y'all don't create the report directly from the Operation Monitor. Instead, from the Beginning screen blazon perfmon /study and click the "perfmn /study" icon that appears on the left. (Annotation that you lot might need Administrator rights to your PC to run the study.) A screen appears telling y'all that a study is generated, and afterwards a minute or two, an interactive report appears onscreen.
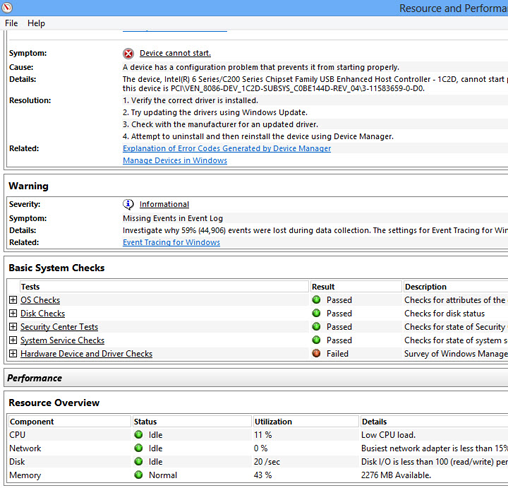
The written report can be lengthy, and goes into mind-numbing detail about your system. (If yous want to know about things such as your system'southward video classes and UDP information it's the place to go.) Most useful are reports of errors or problems. If it finds any, those will be at the very beginning of the written report. For each fault or problem, it describes the symptom and the cause, suggests how to set up it, and provides a link to other useful information.
Streamline startup
A common cause of organisation slowdowns is programs that load unnecessarily at startup and bog downwardly your system. At that place are several ways to speed up startup.
A good place to beginning is the Task Manager. You've got several different means to launch the Job Manager -- accept your choice:
- Press Ctrl-Shift-Esc.
- Right-click the taskbar on the Desktop and choose Task Manager.
- Type task manager on the Start screen, and click the Task Manager icon that appears on the left under Apps.
- Printing Ctrl-Alt-Del, then choose Task Director from the screen that appears.
- Right-click the lower-left corner of your screen and select Job Managing director.
If you meet the phrase "More than details" at the bottom of the Task Managing director screen, click it. If you run into the phrase "Fewer details" at the lesser of the screen, you're already in the right place.
Now click the Startup tab. You'll see a listing of programs and services that launch when you start Windows. For each i, you lot'll see its proper noun, its publisher, whether it'southward enabled and the "startup touch on" -- how much startup is slowed down by launching it. According to Microsoft's developer site, apps labeled as having loftier startup impact utilize more one second of CPU time or more 3MB of disk I/O at startup, medium-impact apps use 300 to 1000 milliseconds of CPU time or 300KB to 3MB of disk I/O, and low-affect apps use less than 300ms of CPU time and less than 300 KB of disk I/O.
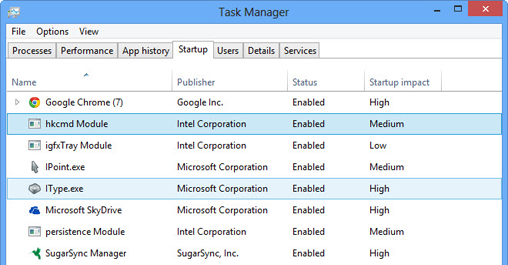
If you'd like to stop any of the programs or services from launching at startup, right-click information technology and select Disable. This doesn't disable the program entirely; it but prevents it from launching at startup. If y'all subsequently determine you desire information technology to launch at startup, get back here, right-click it and select Enable.
Some programs might have a small triangle next to them, indicating that they accept multiple processes that run on startup. Click the triangle to encounter all the processes. It's not a good thought to disable some simply not others, because that could crusade instability in the program. And then either disable all the processes or none.
You'll probable recognize some of the programs and services that run at startup, such as SkyDrive. But you'll also probably come across many that aren't familiar to you and whose purpose is almost impossible to discern. What to do nearly something called "persistence Module" or "hkcmd Module?" Should yous turn them off or leave them on?
The Task Manager offers some solid assistance. Right-click an detail and select Properties, and yous'll see more than detail about it, including its location, whether it has a digital signature from a visitor yous know and other data such as the version number, its size and the last fourth dimension information technology was modified.
Alternatively, when you right-click you tin select "Open file location" and you'll open File Explorer to the folder where the file is located. That may requite you a clue nearly the program'south purpose.
Best of all, though, is to select "Search online" after you right-click. Bing launches and provides links to sites with information well-nigh the program or service. Yous'll usually very quickly find out data most the item, including its purpose and communication on whether it'due south rubber.
For more than ways to apply the Chore Director to speed upwards your system, encounter "Rail and fine-tune performance with the Chore Director" later in this article.
Clean out the Startup binder
There's another identify to become if yous want to finish programs from launching when you lot start your system -- the Startup binder. You lot can run File Explorer in ane of these ways:
- Press the Windows key + E.
- Click the File Explorer icon on the Desktop's taskbar.
- Type file explorer on the Get-go screen and click the File Explorer icon that appears on the left.
Make sure yous tin can view hidden files in File Explorer: Click the View tab and check the boxes next to "Hidden items" and "File name extensions" in the Ribbon at the top.
Next, click the Computer icon in the left pane and navigate to:
C:\Users\<em>username</em>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows<br>\Start Menu\Programs\Startup
where username is your Windows logon. Delete the shortcuts of any programs you don't desire to run at startup. Don't worry; you won't delete the programs themselves, only their shortcuts.
Use Fast Startup
There's one terminal startup item to cheque: Make sure that Windows 8 uses a new way called Fast Startup, a hybrid of a traditional shutdown/boot operation and hibernation. When yous close down your PC, all user sessions are closed only the Windows kernel session is saved to disk, or hibernated. And so when you start Windows again, information technology loads the hibernated system session from deejay, cutting startup time.
By default, Fast Startup should be enabled on your system. But information technology's a good idea to make sure it'southward turned on, just in instance your system wasn't prepare upward correctly or Fast Startup was accidentally turned off.
On the Kickoff screen, type power, click Settings and click the Ability Options icon that appears on the left side of the screen under Settings. Click "Choose what the ability buttons exercise" in the left pane, and under "Shutdown settings" at the bottom of the screen that appears, brand sure that the box next to "Turn on fast startup" is checked.
Source: https://www.computerworld.com/article/2484556/microsoft-windows-how-to-boost-windows-8-performance.html
Posted by: hansenmirere.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Run Windows 8 Faster"
Post a Comment